| Dr. Serruys discussed
the current diagnostic and therapeutic areas important for cardiologists,
and their future use. These include the myocardial infarction center;
new technologies for the diagnosis and treatment of plaque such as
the ecothermal catheter; new imaging techniques such as high resolution
black blood imaging, multi-slide spiral computer tomography, and non-ionizing
imaging; myocardial infarction tissue repair, and a future invention
of an automated device control.
Dr. Andreas Grüntzig was the designer of the modern angioplasty
procedure. In that light, Dr. Serruys discussed current and future
procedures, diagnostics and therapies important for cardiologists.
These include the myocardial infarction center, technologies for
diagnosis of plaque, new imaging techniques, myocardial infarction
tissue repair and his dream of an automated device control.
Dr. Serruys indicated the myocardial infarction center improves
treatment for patients with this illness, as currently demonstrated
in Rotterdam. Upon admission to the hospital, patients are admitted
to a special myocardial infarction unit. Patients are treated and
sent to community hospitals for additional treatment or monitoring.
New diagnostic techniques are emerging to detect plaque and include
tomography and elastography sheer stress imaging. Dr. Serruys discussed
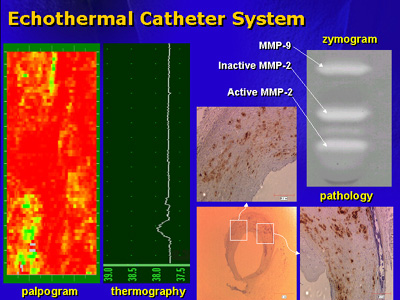
the use of the echothermal catheter in diagnosing plaque. This catheter
is capable of multi-point tomography, simultaneous ultrasonic assessment
of vascular stress/strain relationships and a temperature measurement.
Temperature is important because an increase in plaque temperature
of 0.5 degrees increases the risk of adverse cardiac events. This
device images plaque and identifies the tissue in a vessel such
as fat, fibrous tissue or the normal vessel wall. The catheter is
currently being tested in humans, for widespread plaque the treatment
is pharmacologic therapy. If plaque is isolated, catheter-based
treatment is available.
Many imaging techniques are used to visualize plaque. These include
magnetic resonance imaging, high resolution black blood imaging,
multi-slide spiral computer tomography, and non-ionizing imaging.
Dr. Serruys noted the advantages and disadvantages of each of these
techniques. For example, while magnetic resonance imaging does not
use radiation or contrast media, it has low resolution and reliability.
Multi-slide spiral computer tomography uses contrast media and x-rays,
but has high spatial resolution. This image visualizes the content
of plaque such as calcium or soft tissue. Imaging can be used as
a diagnostic tool or as treatment. Dr. Serruys believes non-ionizing
imaging will guide all interventions because it can be repeated
multiple times, has unlimited exposure time and reveals a 3-D image.
The repair of tissue damaged by myocardial infarction is in clinical
trial in France. This technique injects autologous myoblasts into
injured myocardium. The myocardial tissue regenerates and reestablishes
electrical connections. Patients show symptomatic improvement with
an increased ejection fraction of 13%.
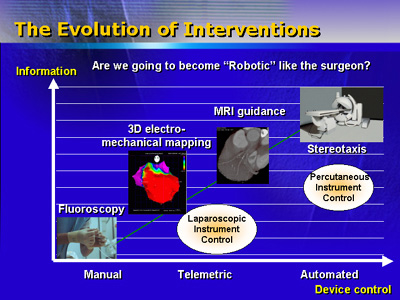
Dr. Serruys imagines an automated device may someday be available
to treat occluded blood vessels. This device would use imaging to
navigate through blood vessels with a magnetic catheter and an ablating
device. The operator would use a joystick to direct the catheter
and ablate the occlusion.
|